<%NUMBERING1%>.<%NUMBERING2%>.<%NUMBERING3%> PRTG Manual: Dropbox Sensor
The Dropbox sensor monitors a Dropbox account using the Dropbox Application Programming Interface (API) and OAuth2. It shows the following:
- Free storage in bytes and percent
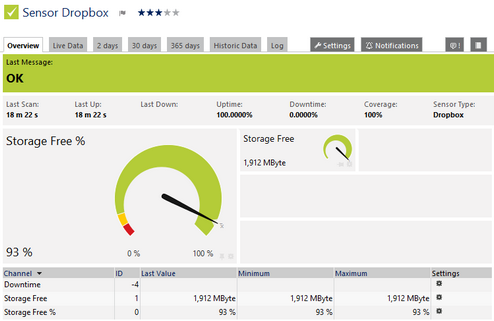
Dropbox Sensor
Click here to enlarge: http://media.paessler.com/prtg-screenshots/dropbox.png
- The minimum scanning interval for this sensor type is 30 minutes.
- For details about OAuth2 authentication, please see manual section Authentication Using OAuth2.
The Add Sensor dialog appears when adding a new sensor on a device manually. It only shows the setting fields that are imperative for creating the sensor. Therefore, you will not see all setting fields in this dialog. You can change (nearly) all settings in the sensor's Settings tab later.
PRTG requires OAuth2 authorization before you can actually add this sensor type. Provide the requested credentials in the appearing window. The following settings for this sensor differ in the 'Add Sensor' dialog in comparison to the sensor's settings page:
Dropbox Credentials |
|
|---|---|
This sensor type uses OAuth2 authentication to get access to your Dropbox account. For details about the authentication approach, please see section Authentication Using OAuth2. |
|
OAuth URL |
Click the button Get Access Code to connect this sensor to your Dropbox account using OAuth2. This is necessary to allow the sensor to query data from Dropbox. A new browser window appears. Please follow the steps there and confirm the permission for PRTG to connect to your Dropbox account. Copy the OAuth code you get and paste it into the OAuth Code field below. |
OAuth Code |
Paste the access code that you receive after completing the authorization process for PRTG at your Dropbox account. Click OK to define the sensor settings. Note: It is mandatory to connect this sensor to your Dropbox account to create this sensor. Please complete the OAuth approach first to get the OAuth code. |
On the details page of a sensor, click on the Settings tab to change its settings.
Note: Usually, a sensor connects to the IP Address or DNS Name of the parent device on which you created this sensor. See the Device Settings for details. For some sensor types, you can define the monitoring target explicitly in the sensor settings. Please see below for details on available settings.
Basic Sensor Settings |
|
|---|---|
Sensor Name |
Enter a meaningful name to identify the sensor. By default, PRTG shows this name in the device tree, as well as in alarms, logs, notifications, reports, maps, libraries, and tickets. |
Parent Tags |
Shows Tags that this sensor inherits from its parent device, group, and probe. This setting is shown for your information only and cannot be changed here. |
Tags |
Enter one or more Tags, separated by space or comma. You can use tags to group sensors and use tag–filtered views later on. Tags are not case sensitive. We recommend that you use the default value. You can add additional tags to it, if you like. Other tags are automatically inherited from objects further up in the device tree. These are visible above as Parent Tags. |
Priority |
Select a priority for the sensor. This setting determines where the sensor is placed in sensor lists. Top priority is at the top of a list. Choose from one star (low priority) to five stars (top priority). |
Dropbox Credentials |
|
|---|---|
OAuth Code |
Shows the authorization code that the sensor uses to get access to your Dropbox account. Once a sensor is created, you cannot change this value. It is shown for reference purposes only. If you need to change this, please add the sensor anew. |
Sensor Display |
|
|---|---|
Primary Channel |
Select a channel from the list to define it as the primary channel. In the device tree, the last value of the primary channel will always be displayed below the sensor's name. The available options depend on what channels are available for this sensor. Note: You can set another primary channel later by clicking on the pin symbol of a channel in the sensor's Overview tab. |
Chart Type |
Define how different channels will be shown for this sensor.
|
Stack Unit |
This setting is only available if stacked graphs are selected above. Choose a unit from the list. All channels with this unit will be stacked on top of each other. By default, you cannot exclude single channels from stacking, if they use the selected unit. However, there is an advanced procedure to do so. |
By default, all following settings are inherited from objects higher in the hierarchy and should be changed there, if necessary. Often, best practice is to change them centrally in the Root group's settings. To change a setting only for this object, disable inheritance by clicking on the check mark before the corresponding setting name. You will then see the options described below.
Scanning Interval |
|
|---|---|
Scanning Interval |
Select a scanning interval (seconds, minutes, or hours) from the list. The scanning interval determines the time the sensor waits between two scans. You can change the available intervals in the system administration. |
When a Sensor Reports an Error |
Define the number of scanning intervals that a sensor has time to report an error before the sensor will be set to a Down status. The sensor can try to reach a device several times, depending on the setup you can specify here, to help avoid false alarms if the monitored device has only temporary issues. For previous scanning intervals with failed requests, the sensor will show a Warning status. Choose between:
Note: Sensors that monitor via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) always wait at least one scanning interval until they show an error. It is not possible to set a WMI sensor "down" immediately, so the first option will not apply to these sensor types (all other options can apply). Note: If a sensor has defined error limits for channels, this sensor will always be set to a Down status immediately, so no "wait" option will apply. Note: If a channel uses lookup values, the sensor will always be set to a Down status immediately, so no "wait" options will apply. |
Note: This sensor type has a fixed minimum scanning interval for performance reasons. You cannot run the sensor in shorter intervals than this minimum interval. Consequently, shorter scanning intervals as defined in System Administration—Monitoring are not available for this sensor.
Schedules, Dependencies, and Maintenance Window |
|
|---|---|
Note: Inheritance for schedules, dependencies, and maintenance windows cannot be interrupted. The corresponding settings from the parent objects will always be active. However, you can define additional settings here. They will be active at the same time as the parent objects' settings. |
|
Schedule |
Select a schedule from the list. Schedules can be used to monitor for a certain time span (days, hours) throughout the week. With the period list option it is also possible to pause monitoring for a specific time span. You can create new schedules and edit existing ones in the account settings. Note: Schedules are generally inherited. New schedules will be added to existing ones, so all schedules are active at the same time. |
Maintenance Window |
Specify if you want to set-up a one-time maintenance window. During a "maintenance window" period, this object and all child objects will not be monitored. They will be in a paused state instead. Choose between:
Note: To terminate a current maintenance window before the defined end date, you can change the time in Maintenance End At field to a date in the past. |
Maintenance Begins At |
This field is only visible if you enabled the maintenance window above. Use the date time picker to enter the start date and time of the maintenance window. |
Maintenance End At |
This field is only visible if you enabled the maintenance window above. Use the date time picker to enter the end date and time of the maintenance window. |
Dependency Type |
Define a dependency type. Dependencies can be used to pause monitoring for an object depending on the status of another. You can choose between:
Note: Testing your dependencies is easy! Simply choose Simulate Error Status from the context menu of an object that other objects depend on. A few seconds later all dependent objects should be paused. You can check all dependencies in your PRTG installation by selecting Devices | Dependencies from the main menu bar. |
Dependency |
This field is only visible if the Select object option is enabled above. Click on the reading-glasses and use the object selector to choose an object on which the current sensor will depend. |
Delay (Seconds) |
Define a time span. After the master object for this dependency comes back to an Up status, the beginning of the monitoring of the depending objects will be additionally delayed by the time span you define here. This can help to avoid false alarms, for example, after a server restart, by giving systems more time for all services to start up. Please enter an integer value in seconds. Note: This setting is not available if you choose this sensor to be the Master object for parent. In this case, please define delays in the parent Device Settings or in the superior Group Settings. |
Access Rights |
|
|---|---|
User Group Access |
Define which user group(s) will have access to the object you're editing. A table with user groups and types of access rights is shown: It contains all user groups from your setup. For each user group you can choose from the following access rights:
You can create new user groups in the System Administration—User Groups settings. To automatically set all objects further down in the hierarchy to inherit this object's access rights, set a check mark for the Revert children's access rights to inherited option. For more details on access rights, please see the section User Access Rights. |
Channel Unit Configuration |
|
|---|---|
Channel Unit Types |
For each type of sensor channel, define the unit in which data is displayed. If defined on probe, group, or device level, these settings can be inherited to all sensors underneath. You can set units for the following channel types (if available):
Note: Custom channel types can be set on sensor level only. |
This sensor type uses the OAuth2 security protocol to access the account from which you want to retrieve and monitor data. OAuth2 enables you to grant access to the target account without sharing your password with PRTG. In general, the authorization approach of PRTG using OAuth2 works like this:
- Authorization Request
First, you have to request authorization for this sensor to access service resources from your account. For this purpose you are asked to get an access code for this sensor in the Add Sensor dialog. Click the Get Access Code button to start the authorization process using OAuth2. This opens a new browser window on the authorization server of the target service. - Verifying Identity
This new window contains a login form for your account that you want to monitor. Log in to your account using your credentials for this service to authenticate your identity. This is a common login to your account on the target server so PRTG will not see your password. The service will forward you to the authorization page and asks you to permit PRTG to access the data in your account.
Note: If you are already logged in to the service with a user account, you do not have to enter credentials in this step and get directly to the access permission page. - Authorizing PRTG
Permit PRTG to access information on your account. Note that this permission holds only for this specific sensor, not for PRTG as a whole. For each sensor of this type you add, you have to confirm the access permission anew. You can change the account permissions at any time in your account at the target service. - Getting Authorization Code
Permitting PRTG to access your account data forwards you to a page where the service provides an authorization code. Copy this code and switch back to the Add Sensor dialog in PRTG.
Note: The code is valid only a short period of time and expires after a few minutes. You can use a particular code only once. - Providing Authorization Code
Paste the authorization code into the OAuth Code field and complete the Add Sensor dialog. You do not have to go through further configuration steps manually. The sensor will accomplish the following steps automatically. - Requesting Access Token
After getting the authorization code, PRTG requests an access token from the API of the target service. For this purpose PRTG transmits the authorization code together with several authentication details. The API checks if the authorization is valid and returns the access token to PRTG. Access token are specific for one account and one application (here: PRTG). The authorization process to read data from your account is now complete. - Retrieving Data
The sensor transmits the access token with each sensor scan in the defined scanning interval to authenticate at your account. It is not necessary to use the original account credentials anew. The used tokens are refreshed automatically from time to time.
To change display settings, spike filter, and limits, switch to the sensor's Overview tab and click the gear icon of a specific channel. For detailed information, please see the Sensor Channels Settings section.
Click the Notifications tab to change notification triggers. For detailed information, please see the Sensor Notifications Settings section.
For more general information about settings, please see the Object Settings section.
For information about sensor settings, please see the following sections:
Keywords: