<%NUMBERING1%>.<%NUMBERING2%>.<%NUMBERING3%> PRTG Manual: HTTP Data Advanced Sensor
The HTTP Data Advanced sensor accesses a web server and retrieves XML or JSON encoded data. For details about the return value format, please see the Application Programming Interface (API) Definition.
- The sensor can show values returned by the web server in multiple channels.
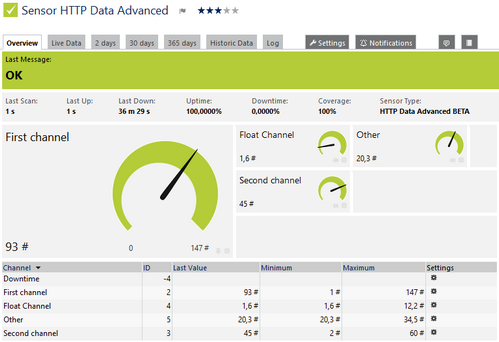
HTTP Data Advanced Sensor
Click here to enlarge: http://media.paessler.com/prtg-screenshots/http_data_advanced.png
- The requested web server must return XML or JSON encoded data that matches the format as defined in the API documentation in section Custom Sensors—Advanced EXE/Script Sensor, Advanced SSH Script Sensor, and Advanced HTTP Push Data Sensor.
- For best sensor performance, we recommend that you specify the content type on the target server, which is application/xml or application/json.
- Note: You do not have to define the sensor behavior for HTTP result codes. For details, see this Knowledge Base article: Which HTTP status code leads to which HTTP sensor status?
- Note: This sensor type does not support Secure Remote Password (SRP) ciphers.
- Important notice: Currently, this sensor type is in beta status. The methods of operating can change at any time, as well as the available settings. Do not expect that all functions will work properly, or that this sensor works as expected at all. Be aware that this type of sensor can be removed again from PRTG at any time.
The Add Sensor dialog appears when adding a new sensor on a device manually. It only shows the setting fields that are imperative for creating the sensor. Therefore, you will not see all setting fields in this dialog. You can change (nearly) all settings in the sensor's Settings tab later.
On the details page of a sensor, click on the Settings tab to change its settings.
Note: Usually, a sensor connects to the IP Address or DNS Name of the parent device on which you created this sensor. See the Device Settings for details. For some sensor types, you can define the monitoring target explicitly in the sensor settings. Please see below for details on available settings.
Basic Sensor Settings |
|
|---|---|
Sensor Name |
Enter a meaningful name to identify the sensor. By default, PRTG shows this name in the device tree, as well as in alarms, logs, notifications, reports, maps, libraries, and tickets. |
Parent Tags |
Shows Tags that this sensor inherits from its parent device, group, and probe. This setting is shown for your information only and cannot be changed here. |
Tags |
Enter one or more Tags, separated by space or comma. You can use tags to group sensors and use tag–filtered views later on. Tags are not case sensitive. We recommend that you use the default value. You can add additional tags to it, if you like. Other tags are automatically inherited from objects further up in the device tree. These are visible above as Parent Tags. |
Priority |
Select a priority for the sensor. This setting determines where the sensor is placed in sensor lists. Top priority is at the top of a list. Choose from one star (low priority) to five stars (top priority). |
HTTP Specific |
|
|---|---|
Timeout (Sec.) |
Enter a timeout in seconds for the request. If the reply takes longer than this value defines, the sensor will cancel the request and show a corresponding error message. Please enter an integer value. The maximum value is 900 seconds (15 minutes). |
URL |
Enter the URL the sensor connects to. It has to be URL encoded! If you enter an absolute URL, the sensor uses this address independently from the IP address/DNS name setting of the device on which you create this sensor. PRTG uses a smart URL replacement which allows you to use the parent device's IP Address/DNS Name setting as part of the URL. For more information, please see section Smart URL Replacement below. |
Request Method |
Choose an HTTP request method to determine how the sensor will request the given URL.
|
Postdata |
This field is only visible if you select the POST method above. Enter the data part for the POST request here. Note: No XML is allowed here! |
Result Handling |
Define what the sensor will do with the data loaded at the given URL. Choose between:
|
Authentication |
|
|---|---|
Authentication |
Define if the web page at the configured URL needs authentication. Choose between:
|
User |
This field is only visible if you enable authentication above. Enter a username. Please enter a string. |
Password |
This field is only visible if you enable authentication above. Enter a password. Please enter a string. |
Authentication Method |
This field is only visible if enable authentication above. Select the authentication method the given URL is protected with. Choose between:
We recommend that you use the default value. |
Sensor Display |
|
|---|---|
Primary Channel |
Select a channel from the list to define it as the primary channel. In the device tree, the last value of the primary channel will always be displayed below the sensor's name. The available options depend on what channels are available for this sensor. Note: You can set another primary channel later by clicking on the pin symbol of a channel in the sensor's Overview tab. |
Chart Type |
Define how different channels will be shown for this sensor.
|
Stack Unit |
This setting is only available if stacked graphs are selected above. Choose a unit from the list. All channels with this unit will be stacked on top of each other. By default, you cannot exclude single channels from stacking, if they use the selected unit. However, there is an advanced procedure to do so. |
By default, all following settings are inherited from objects higher in the hierarchy and should be changed there, if necessary. Often, best practice is to change them centrally in the Root group's settings. To change a setting only for this object, disable inheritance by clicking on the check mark before the corresponding setting name. You will then see the options described below.
Proxy Settings for HTTP Sensors |
|
|---|---|
HTTP Proxy Settings |
The proxy settings determine how a sensor connects to a given URL. You can enter data for a proxy server that will be used when connecting via HTTP or HTTPS. Note: This setting is valid for the monitoring only and determines the behavior of sensors. In order to change proxy settings for the core server, please see System Administration—Core & Probes. |
Name |
Enter the IP address or DNS name of the proxy server to use. If you leave this field empty, no proxy will be used. |
Port |
Enter the port number of the proxy. Often, port 8080 is used. Please enter an integer value. |
User |
If the proxy requires authentication, enter the username for the proxy login. Note: Only basic authentication is available! Please enter a string or leave the field empty. |
Password |
If the proxy requires authentication, enter the password for the proxy login. Note: Only basic authentication is available! Please enter a string or leave the field empty. |
Scanning Interval |
|
|---|---|
Scanning Interval |
Select a scanning interval (seconds, minutes, or hours) from the list. The scanning interval determines the time the sensor waits between two scans. You can change the available intervals in the system administration. |
When a Sensor Reports an Error |
Define the number of scanning intervals that a sensor has time to report an error before the sensor will be set to a Down status. The sensor can try to reach a device several times, depending on the setup you can specify here, to help avoid false alarms if the monitored device has only temporary issues. For previous scanning intervals with failed requests, the sensor will show a Warning status. Choose between:
Note: Sensors that monitor via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) always wait at least one scanning interval until they show an error. It is not possible to set a WMI sensor "down" immediately, so the first option will not apply to these sensor types (all other options can apply). Note: If a sensor has defined error limits for channels, this sensor will always be set to a Down status immediately, so no "wait" option will apply. Note: If a channel uses lookup values, the sensor will always be set to a Down status immediately, so no "wait" options will apply. |
Schedules, Dependencies, and Maintenance Window |
|
|---|---|
Note: Inheritance for schedules, dependencies, and maintenance windows cannot be interrupted. The corresponding settings from the parent objects will always be active. However, you can define additional settings here. They will be active at the same time as the parent objects' settings. |
|
Schedule |
Select a schedule from the list. Schedules can be used to monitor for a certain time span (days, hours) throughout the week. With the period list option it is also possible to pause monitoring for a specific time span. You can create new schedules and edit existing ones in the account settings. Note: Schedules are generally inherited. New schedules will be added to existing ones, so all schedules are active at the same time. |
Maintenance Window |
Specify if you want to set-up a one-time maintenance window. During a "maintenance window" period, this object and all child objects will not be monitored. They will be in a paused state instead. Choose between:
Note: To terminate a current maintenance window before the defined end date, you can change the time in Maintenance End At field to a date in the past. |
Maintenance Begins At |
This field is only visible if you enabled the maintenance window above. Use the date time picker to enter the start date and time of the maintenance window. |
Maintenance End At |
This field is only visible if you enabled the maintenance window above. Use the date time picker to enter the end date and time of the maintenance window. |
Dependency Type |
Define a dependency type. Dependencies can be used to pause monitoring for an object depending on the status of another. You can choose between:
Note: Testing your dependencies is easy! Simply choose Simulate Error Status from the context menu of an object that other objects depend on. A few seconds later all dependent objects should be paused. You can check all dependencies in your PRTG installation by selecting Devices | Dependencies from the main menu bar. |
Dependency |
This field is only visible if the Select object option is enabled above. Click on the reading-glasses and use the object selector to choose an object on which the current sensor will depend. |
Delay (Seconds) |
Define a time span. After the master object for this dependency comes back to an Up status, the beginning of the monitoring of the depending objects will be additionally delayed by the time span you define here. This can help to avoid false alarms, for example, after a server restart, by giving systems more time for all services to start up. Please enter an integer value in seconds. Note: This setting is not available if you choose this sensor to be the Master object for parent. In this case, please define delays in the parent Device Settings or in the superior Group Settings. |
Access Rights |
|
|---|---|
User Group Access |
Define which user group(s) will have access to the object you're editing. A table with user groups and types of access rights is shown: It contains all user groups from your setup. For each user group you can choose from the following access rights:
You can create new user groups in the System Administration—User Groups settings. To automatically set all objects further down in the hierarchy to inherit this object's access rights, set a check mark for the Revert children's access rights to inherited option. For more details on access rights, please see the section User Access Rights. |
Channel Unit Configuration |
|
|---|---|
Channel Unit Types |
For each type of sensor channel, define the unit in which data is displayed. If defined on probe, group, or device level, these settings can be inherited to all sensors underneath. You can set units for the following channel types (if available):
Note: Custom channel types can be set on sensor level only. |
Instead of entering a complete address in the URL field of an HTTP sensor, you can merely enter the protocol followed by colon and three slashes (that means you can enter either http:/// or https:/// or even a simple slash / as equivalent for http:///). PRTG will then fill in the parent device's IP address or DNS name in front of the third slash automatically. Whether this results in a valid URL or not, depends on the IP address or DNS name of the device where this HTTP sensor is created on. In combination with cloning devices, the smart URL replacement makes it easy to create many like devices.
For example, if you create a device with DNS name www.example.com and you put an HTTP sensor on it, you can provide values the following ways:
- Providing the value https:/// in the URL field, PRTG will automatically create the URL https://www.example.com/ from that.
- Using the value /help in the URL field, PRTG will automatically create and monitor the URL http://www.example.com/help
- It is also possible to provide a port number in the URL field which will be taken over by the device's DNS name and internally added, for example, http://:8080/
Note: Smart URL replacement does not work for sensors running on the "Probe Device".
Knowledge Base: Which HTTP status code leads to which HTTP sensor status?
To change display settings, spike filter, and limits, switch to the sensor's Overview tab and click the gear icon of a specific channel. For detailed information, please see the Sensor Channels Settings section.
Click the Notifications tab to change notification triggers. For detailed information, please see the Sensor Notifications Settings section.
For more general information about settings, please see the Object Settings section.
For information about sensor settings, please see the following sections:
Keywords: